How Much Protein Do You Need to Build Muscle?

Protein brings the gains – we know that.
But what a lot of us are confused about is just how, why, the amount we need, the factors that affect how much we need, and where we can best get it from. In this article, we’ll cover how much protein to build muscle and the easiest way to do it.
First things first though…
Protein is super important for muscle growth because it provides the key building blocks for muscle growth.
That’s why everyone obsesses over it!
Alright, let's take a deeper look now at it all.

The importance of protein in muscle building
So why is protein so good for muscle growth? And not carbs or fat?
Well, protein contains amino acids, notably, leucine, which is critical for muscle growth. When we smash out a gym session, having put stress on our muscles, they break down and need protein to rebuild and grow stronger.
And these amino acids aren’t found in carbs and fats.
When the rate of our protein consumption outweighs muscle breakdown, that’s when we rebuild and repair muscle. And that’s when we grow.
Sort of like business: when we make more money than we spend, we profit!
So that’s why everyone gets excited about protein for muscle growth.

The different types of protein
Protein powder has a higher biological value compared to food sources of protein.
This is because protein powder is typically processed to concentrate and isolate specific amino acids, removing any non-protein components that may interfere with absorption. As a result, protein powders are more easily utilised for muscle building and repair.
Additionally, protein powders offer a convenient and consistent source of protein that can be easily incorporated into a muscle growth workout plan.
But remember: this doesn’t mean we should shun chicken, meat, dairy, eggs, and plant-based sources, as we need a balanced diet – supplements are for convenience and to supplement our protein needs when it's difficult to get them!
Alright, let’s now take a look at how much protein you need for bulking.
How much protein do you need?
How much protein do I need for muscle growth is one of the most common questions for anyone starting out. An even more common question is how much protein per kg.
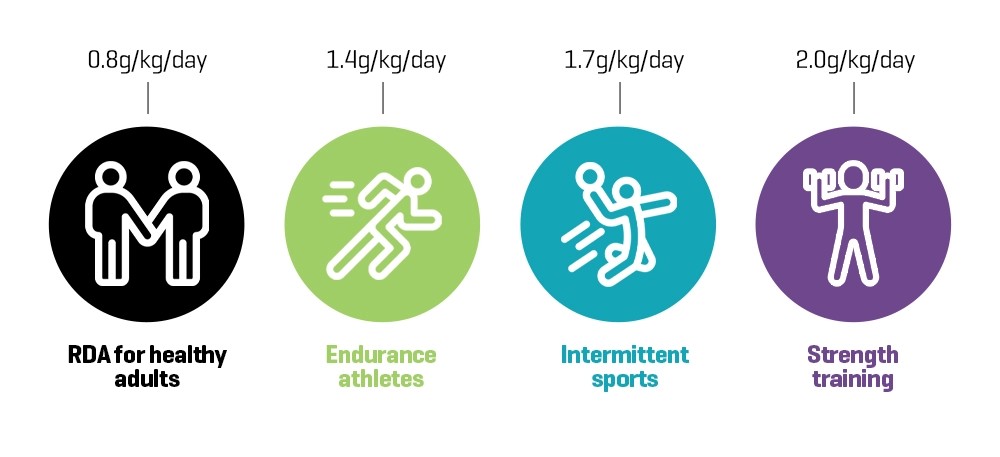
Well, according to recent scientific recommendations, the daily protein intake for muscle growth varies based on an individual's body weight and physical activity level.
But because you’re looking to grow muscle mass, it’s recommended we consume ~2.2 grams of protein per kg of weight per day. That’s how much protein a day to build muscle.
How much protein per meal?
Based on the current evidence, to maximise muscle growth you should consume protein at a target intake of 0.55 grams of protein per kg of weight per meal, spread out over four meals.
This helps you achieve the aforementioned daily intake of 2.2 grams of protein per kg of weight per day. That’s how much protein per day for muscle growth.
Tips for incorporating more protein in your diet
Here are 8 tips to keep in mind when planning protein intake for muscle growth:
- Include protein-rich foods in every meal, such as eggs, dairy products, poultry, fish, and lean meats.
- Make protein-rich snacks like nuts, seeds, and protein bars.
- Get one of our protein powder supplements – to make smoothies or baked goods to increase protein content.
- Use plant-based proteins like tofu, tempeh, or legumes, in your meals.
- Choose dairy products like milk, yogurt, and cheese, which are high in protein.
- Replace high-carbohydrate snacks with protein-rich options like cheese sticks or boiled eggs.
- Consider eating a protein-rich breakfast, such as eggs or a protein supplement
- Plan your meals in advance and always make sure to include protein sources.
Factors that affect protein needs
We’re all different when it comes to protein needs; they vary depending on factors like age, weight, activity level, and muscle mass.
Generally, a sedentary adult requires about 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, while athletes and highly active individuals may require more. As we age, our muscle mass decreases, therefore older individuals may need more protein to maintain and rebuild muscle.
Weight also plays a role, as individuals with higher body weight require more protein.
Finally, activity level affects protein needs, such as you performing intense lifting to grow muscle mass - which requires more protein for growth and repair.
Tips for determining your individual protein needs
To know just how much protein you need, consider these steps:
- To determine protein needs, you need to first calculate your daily caloric needs based on your age, weight, height, and activity level.
- Consider your muscle mass: The more muscle mass you have, the more protein you need to support muscle growth and repair. So 2.2 grams of protein per kg of body weight per day is ideal.
- Account for your activity level: if you engage in regular physical activity you’ll need more protein than sedentary individuals. Again, go for the 2.2 grams of protein per kg of body weight per day here.
- Consider your weight loss or gain goals: If you're trying to lose weight, you’ll actually need more protein for satiety.
So, there’s some bullet-proof info on the importance of protein in muscle building, and how protein provides the key building blocks for muscle growth in the form of amino acids, particularly leucine.
You now know more about the different types of protein, with protein powder being seen as the most convenient and efficient option, but a balanced diet with food sources of protein is still recommended.
Aim for 2.2 grams of protein per kg of weight per day, spread out over four meals for optimal muscle growth results. Remember to incorporate protein-rich foods in every meal, use protein supplements, and plan meals in advance.

Ellie’s an absolute copywriting boss from Hobart, Tasmania!
She's an amateur powerlifter who's crushed it in several competitions, and she's got all the keto knowledge to keep her fuelled up for her workouts.
One thing you'll always find in Ellie's pantry is a jar of peanut butter - she's obsessed.
More about Ellie HearnReferences:
- Bandegan, A., Courtney-Martin, G., Rafii, M., Pencharz, P. and Lemon, P., 2017. Indicator Amino Acid–Derived Estimate of Dietary Protein Requirement for Male Bodybuilders on a Nontraining Day Is Several-Fold Greater than the Current Recommended Dietary Allowance. The Journal of Nutrition, [online] 147(5), pp.850-857. Available at: Indicator Amino Acid–Derived Estimate of Dietary Protein Requirement for Male Bodybuilders on a Nontraining Day Is Several-Fold Greater than the Current Recommended Dietary Allowance.
- Campbell, B., Kreider, R., Ziegenfuss, T., La Bounty, P., Roberts, M., Burke, D., Landis, J., Lopez, H. and Antonio, J., 2007. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: protein and exercise. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, [online] 4(1), p.8. Available at: International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: protein and exercise. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition.
- Leaf, A., 2020. How Much Protein Do You Need Per Day?. [online] Examine.com. Available at: How Much Protein Do You Need Per Day?..
- Patel, K., 2020. A Second Look At Protein Quantity After Exercise. [online] Examine.com. Available at: A Second Look At Protein Quantity After Exercise..
- Nrv.gov.au. 2020. Protein | Nutrient Reference Values. [online] Available at: Protein | Nutrient Reference Values..
- Thomas, D., Erdman, K. and Burke, L., 2016. Nutrition and Athletic Performance. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, [online] 48(3), pp.543-568. Available at: Nutrition and Athletic Performance. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise.
- Mero A. Leucine supplementation and intensive training. Sports Med. 1999 Jun;27(6):347-58. doi: 10.2165/00007256-199927060-00001. PMID: 10418071.
- Tipton KD, Wolfe RR. Exercise, protein metabolism, and muscle growth. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2001 Mar;11(1):109-32. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.11.1.109. PMID: 11255140.
- Hoffman JR, Falvo MJ. Protein - Which is Best? J Sports Sci Med. 2004 Sep 1;3(3):118-30. PMID: 24482589; PMCID: PMC3905294.
- Carbone JW, Pasiakos SM. Dietary Protein and Muscle Mass: Translating Science to Application and Health Benefit. Nutrients. 2019 May 22;11(5):1136. doi: 10.3390/nu11051136. PMID: 31121843; PMCID: PMC6566799.
Related Blogs

How Citrulline Malate May Help You Grow More Muscle
Posted by Dayne Hudson
Estimated reading time: 5 minutes

Does Protein Timing Matter for Muscle Growth?
Posted by Dayne Hudson
Estimated reading time: 4 minutes

Let’s Talk About Genetics…
Posted by Jackson Peos
Estimated reading time: 7 minutes



































